The concept of precision medicine as proposed by DC-ren is also of great interest to SMEs and other academic institutions. In order to allow collaborations, we established the concept of “DC-ren associated studies”.
Currently DC-ren collaborates with the Department of Nephrology, Saarland University Medical Center, Homburg, Germany to evaluate the short and long term prognostic and predictive power of urinary Dickkopf-3 in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
In addition the DC-ren team was approached by Nordic Bioscience® (based in Herlev, Denmark), a company focusing amongst others on biomarkers of extracellular matrix turnover, a pathomechanism of great interest in the context of drug response and DKD progression. The DC-ren consortium and Nordic Bioscience agreed to collaborate on projects looking at the association of novel extracellular matrix turnover biomarkers with cardiorenal outcome and mortality as well as treatment response in patients with diabetes mellitus type 2.
Combination Therapy of RAS Inhibition and SGLT2 Inhibitors Decreases Levels of Endotrophin in Persons with Type 2 Diabetes.
Møller AL, Thöni S, Keller F, Sharifli S, Rasmussen DGK, Genovese F, Karsdal MA, Mayer G.Biomedicines. 2023 Nov 17;11(11):3084. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11113084
Link to publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38002084/)
Extended Abstract 1:
Combination treatment impacts levels of extracellular matrix turnover biomarkers in the drug combinations for rewriting trajectories of renal pathologies in type II diabetes (DC-ren) study.
Møller AL1,2, Thöni S3, Keller F3, Sharifli S3, Karsdal MA1, Genovese F1, Rasmussen DGK1, Mayer G3.
1. Nordic Bioscience A/S, Herlev, Denmark
2. Department of Biomedical Sciences, University of Copenhagen, Denmark
3. Department of Internal Medicine IV (Nephrology and Hypertension), Medical University Innsbruck, Innsbruck, Austria
Background and aim: DC-ren focuses on diabetic kidney disease (DKD), a severe complication of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), often accompanied by cardiovascular disease. Despite currently available therapies, the risk of developing DKD remains high, and the early stage of the disease, as well as disease progression, may go unnoticed until the manifestation of serious complications. Novel biomarkers for identifying patients at an increased risk of disease progression and for predicting a response to treatment are of major importance to develop the concept of precision medicine.
Kidney disease progression is characterized by a progressive deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM) components such as collagen, ultimately resulting in kidney fibrosis. Recently, the ability to quantify key epitopes of collagen fragments generated during ECM turnover emerged.
We aimed to investigate the effect of different combination treatments on two ECM turnover biomarkers in patients with T2DM included in the DC-ren study population.
Description of the biomarkers and previous findings: PRO-C6 reflects active formation of collagen type VI and levels of a signaling fragment, endotrophin (ETP). Levels of ETP (measured by the PRO-C6 ELISA) have been shown to correlate with the extent of tubulointerstitial fibrosis in the kidney, and co-localization of ETP with collagen type VI in the fibrotic kidney has been confirmed. Increased collagen type VI formation has been associated with an increased risk of cardio-renal complications and mortality in patients with diabetes. Elevated levels of ETP at baseline were prognostic for mortality, progression of kidney disease, and cardiovascular events in individuals with and without diabetes.
C3M reflects active degradation of collagen type III mediated by matrix-metalloproteinases. Levels of this biomarker in urine were consistently decreased with progressive chronic kidney disease (CKD) severity in several cohorts of CKD patients.
In the AWARD-7 trial, dulaglutide treatment was associated with ETP and C3M biomarker changes compared to treatment with insulin glargine, suggesting a potential effect to reduce fibrogenesis.
Materials and methods: We measured levels of ETP in plasma and C3M in urine from individuals enrolled in the DC-ren study. Biomarkers were measured at baseline and on average after years 1, 2, and 3. Urinary C3M levels were corrected for urinary creatinine. All individuals were on Renin-angiotensin system inhibitor (RASi) treatment at baseline and during follow-up. While some patients remained on RASi treatment only, others received a combination treatment with either a Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor (SGLT2i) or a Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) on top of RASi treatment.
Findings: ETP was measured in 294 individuals included in the DC-ren study. 102 (35 %) received combination treatment with RASi and SGLT2i during follow-up. The number of follow-ups ranged from one to five, with the majority of the participants (71%) having three annual follow-ups. Baseline characteristics of the patient cohort are displayed in table 1.
Table 1:
Baseline clinical characteristics of the study cohort. Individuals with missing ETP levels at baseline are not shown. Data are n (%), mean ± SD, or median (IQR). BP, blood pressure; UACR, urinary albumin-to-creatinine-ratio.
| ETP > median (n = 119)* | ETP < median (n = 120)* | p-value | |
| Age (years) | 67 ± 10 | 65 ± 7 | 0.134 |
| Female sex | 55 (46) | 65 (54) | 0.272 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 31 ± 5 | 30 ± 4 | 0.105 |
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | 136 ± 13 | 138 ± 18 | 0.226 |
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) | 78 ± 9 | 78 ± 10 | 0.831 |
| eGFR (ml/min/1.73m2) | 59 (45 – 72) | 74 (63 – 81) | < 0.001 |
| UACR (mg/g) | 15 (5-39) | 8 (4-23) | 0.033 |
| Diabetes duration (years) | 14 ± 8 | 13 ± 8 | 0.316 |
| HbA1c (%) | 7.2 ± 1.1 | 7.3 ± 1.3 | 0.429 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dl) | 13.4 ± 1.5 | 13.9 ± 1.4 | 0.013 |
| LDL cholesterol (mg/dl) | 97 ± 36 | 102 ± 41 | 0.297 |
| HDL cholesterol (mg/dl) | 48 ± 15 | 52 ± 15 | 0.083 |
| Serum albumin (g/dl) | 4.5 (4.2 – 4.8) | 4.5 (4.2 – 4.8) | 0.449 |
| Serum potassium (mmol/l) | 4.5 (4.1 – 4.7) | 4.3 (4.1 – 4.6) | 0.141 |
Higher baseline levels of plasma ETP were associated with lower eGFR (p < 0.001) and higher albuminuria (p = 0.03), respectively, and this relation remained consistent over time.
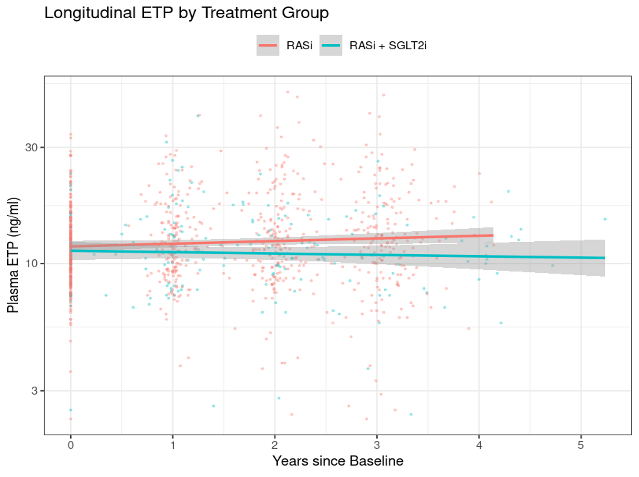
Compared to RASi monotherapy, the combination treatment resulted in a significant reduction of ETP levels (p = 0.002, figure 1), as well as a trend towards a slower eGFR decline, although this trend was not significant (p = 0.074).
Figure 1:
Longitudinal ETP levels by treatment group over time. P-value for slope difference = 0.002.
C3M was measured in 229 individuals included in the DC-ren study. 45 (20 %) received combination treatment with RASi and GLP-1 RA during follow-up. The number of follow-ups ranged from one to five, with the majority of the participants (83 %) having three annual follow-ups. Baseline characteristics of the patient cohort are displayed in Table 2.
Table 2:
Baseline clinical characteristics of the study cohort. Individuals with missing C3M levels at baseline are not shown. Data are n (%), mean ± SD, or median (IQR). BP, blood pressure; UACR, urinary albumin-to-creatinine-ratio.
| C3M > median (n = 114) | C3M < median (n = 115) | p-value | |
| Age (years) | 66 ± 9.02 | 67 ± 8 | 0.89 |
| Female sex | 62 (54) | 57 (50) | 0.55 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 31 ± 5 | 40 ± 5 | 0.572 |
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | 138 ± 16 | 137 ± 16 | 0.429 |
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) | 78 ± 10 | 79 ± 10 | 0.525 |
| eGFR (ml/min/1.73m2) | 68 ± 16 | 61 ± 16 | 0.001 |
| UACR (mg/g) | 12 (5 – 35) | 9 (4 – 26) | 0.29 |
| Diabetes duration (years) | 14 ± 8 | 13 ± 7 | 0.077 |
| HbA1c (%) | 7.4 ± 1.2 | 7.1 ± 1.1 | 0.078 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dl) | 13.5 ± 1.5 | 13.5 ± 1.2 | 0.801 |
| LDL cholesterol (mg/dl) | 96 ± 37 | 102 ± 36 | 0.224 |
| HDL cholesterol (mg/dl) | 51 ± 14 | 50 ± 15 | 0.347 |
| Serum albumin (g/dl) | 4.4 (4.1 – 4.7) | 4.5 (4.3, 4.8) | 0.042 |
| Serum potassium (mmol/l) | 4.4 (4.1 – 4.6) | 4.4 (4.1 – 4.7) | 1 |
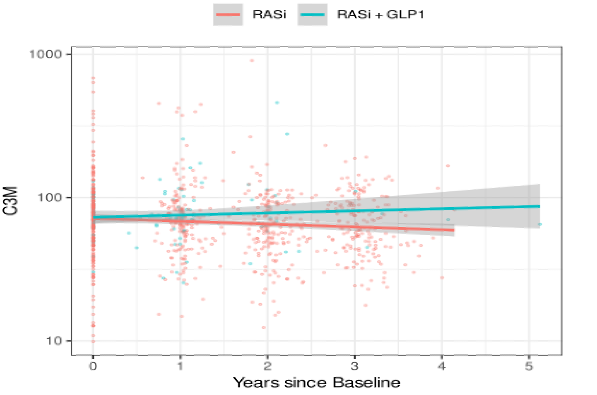
Lower baseline levels of urinary C3M were associated with lower eGFR (p = 0.001), and this relation remained consistent over time. No association of C3M and albuminuria was found. Compared to RASi monotherapy, the combination treatment resulted in a significant increase of C3M compared to RASi alone (p = 0.034, Figure 2).
Figure 2: Longitudinal C3M levels by treatment group over time. P-value for slope difference = 0.034.
In adjusted linear models (for the RASi group), a significant association of current urinary C3M with future eGFR was found (p < 0.01).
Conclusion: Levels of ETP decreased with combination treatment, indicating that RASi in combination with SGLT2i affects collagen type VI formation and levels of ETP. The degree of kidney disease severity increased with increasing plasma levels of ETP at baseline, indicating that the biomarker identifies patients with high disease activity where the potential of an anti-fibrotic effect of treatment becomes more prominent.
Similarly, RASi in combination with GLP-1 RA treatment was associated with increased collagen type III degradation, suggesting a potential effect to reduce progression of kidney fibrosis.
These data suggest that ETP and C3M may serve as prognostic and pharmacodynamic markers in the field of DKD.
A second study will test the prognostic power of endotrophin in the complete PROVALID population.
Endotrophin as a risk marker of cardio-renal outcomes and mortality: A multinational prospective cohort study in persons with type 2 diabetes for validation of biomarkers (PROVALID). A DC-ren associated study.
Møller AL1,2, Thöni S3, Keller F3, Sharifli S3, Karsdal MA1, Genovese F1, Rasmussen DGK1, Mayer G3.
1. Nordic Bioscience A/S, Herlev, Denmark
2. Department of Biomedical Sciences, University of Copenhagen, Denmark
3. Department of Internal Medicine IV (Nephrology and Hypertension), Medical University Innsbruck, Innsbruck, Austria
Background and aim: Type 2 diabetes (T2DM) is the main cause for the development of kidney failure with replacement therapy (KFRT). The progression of kidney disease is characterized by an increasing deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins, such as collagens, leading to fibrosis. The extent of tubulointerstitial fibrosis is a powerful predictor for progressive kidney function loss. Our goal is to determine the value of the ETP biomarker, reflecting active collagen type VI formation and levels of a signaling fragment, endotrophin (ETP), as a risk marker of renal and cardiovascular outcomes, and all-cause-mortality in the PROVALID cohort.
Materials and methods: PROVALID is a prospective cohort study that recruited 4,000 patients with incident or prevalent T2DM, irrespective of the presence of chronic kidney disease. Blood samples, laboratory parameters, and information on potential study outcomes were collected at baseline and during annual follow-up visits. Detailed information on study design and patient characteristics has been described elsewhere. Plasma levels of ETP (measured by the PRO-C6 ELISA) at baseline were measured in all eligible patients with sufficient follow-up data. To evaluate the relationship between baseline ETP and outcomes, we will perform univariate and multivariate regression analyses, as well as Cox proportional hazard regressions. This analysis will determine whether baseline levels of ETP in plasma of patients with T2DM are prognostic for unfavourable outcomes in this highly vulnerable population.


